- Op-Ed
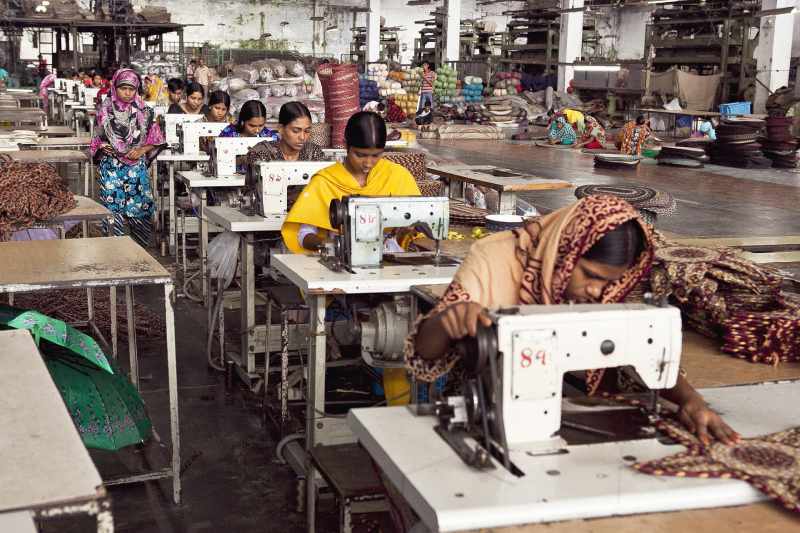
Uncertainty lifted on February 2nd, 2026, as the President Trump announced reduction of tariffs on Indian goods to 18% from more than 50% earlier. Mihir Parekh and Nitya Srinath explain that while the details are awaited, this is a breakthrough moment for Indian exports in general and labour intensive exports in particular.
- February 9, 2026